One of the most innovative and influential chapters in the history of creativity is called modern art. Modern art exists as a diverse collection of artistic movements that revolutionized the art world. Artists launched a revolution of innovation through their rejection of traditional rules to create new ways of expressing color and form, and emotional depth. Modern art takes viewers on a hundred-year exploration of creative explosions through the dreamlike Surrealist worlds and the bold Pop Art statements, and the Impressionist scenes with their blurry light-filled effects.
The beginning of modern art requires understanding its origins as a rebellion against pre-existing artistic approaches. For centuries, the art world operated under academic art principles which emphasized tradition alongside skill and realistic depictions. Artists received training to create historical scenes and religious figures, and portraits, which needed flawless detail and perspective. The artistic objective involved creating an immaculate, life-like deception on canvas.
Artists of the 1860s and 1870s created a fresh artistic approach that opposed the rigid artistic standards that dominated during that period. The artists believed that art needed to move beyond its function because it should express the artist’s individual experiences and intellectual and emotional perspectives. The development of an intellectual mindset resulted in what we identify as the modern art movement. The period of artistic innovation and experimentation known as modern art existed as a continuous development throughout the 1860s until the 1970s.
Artists united to reject historical approaches while developing innovative methods for representing the world during this period. Modern artists redirected their creative focus away from traditional subjects by studying the landscapes and urban environments, together with everyday life.
The fundamental concept of modern art involves breaking conventions through innovative practices. Artists started to challenge the fundamental reasons behind art creation. Paintings need to appear realistic to fulfill their purpose. Artists could use exaggerated colors to represent emotions or they used distorted shapes to express motion.
The following artistic movements resulted in rapid artistic development. And the cultural transformation of this period duplicated the social changes, which included scientific progress, technological advancements, political transformations and societal developments. Art was transformed by the modern art movement to meet the demands of the contemporary era.
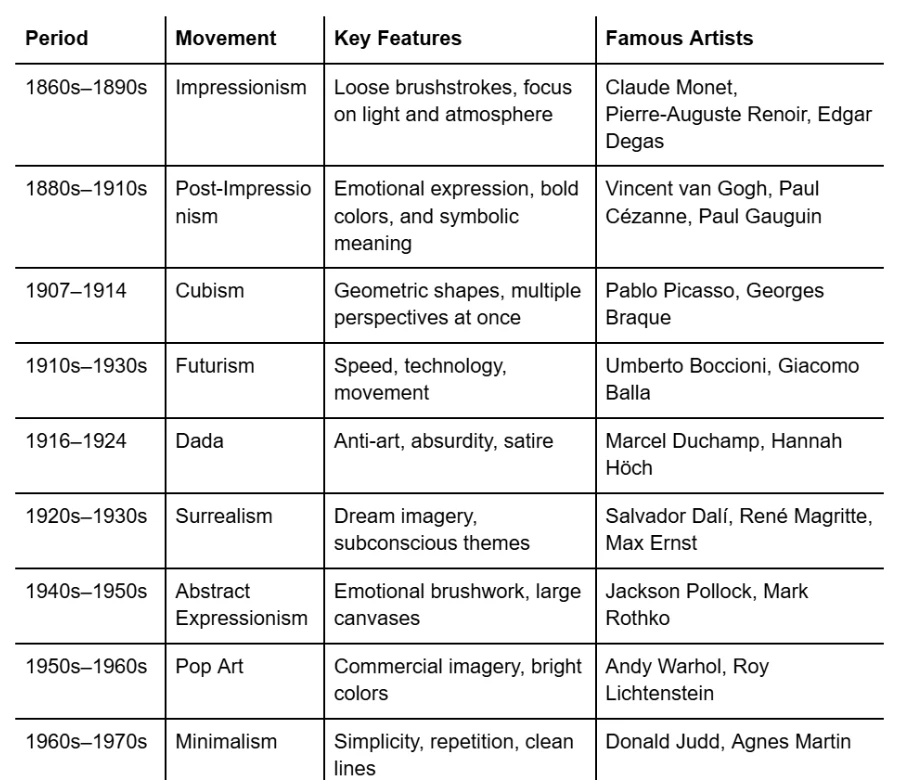
The contemporary art world has many influential modern painting styles that emerged from multiple artistic movements. Each style revolutionized artistic thinking in the modern era, which continues to influence present-day perceptions of creative expression. Here are the 6 modern art styles:
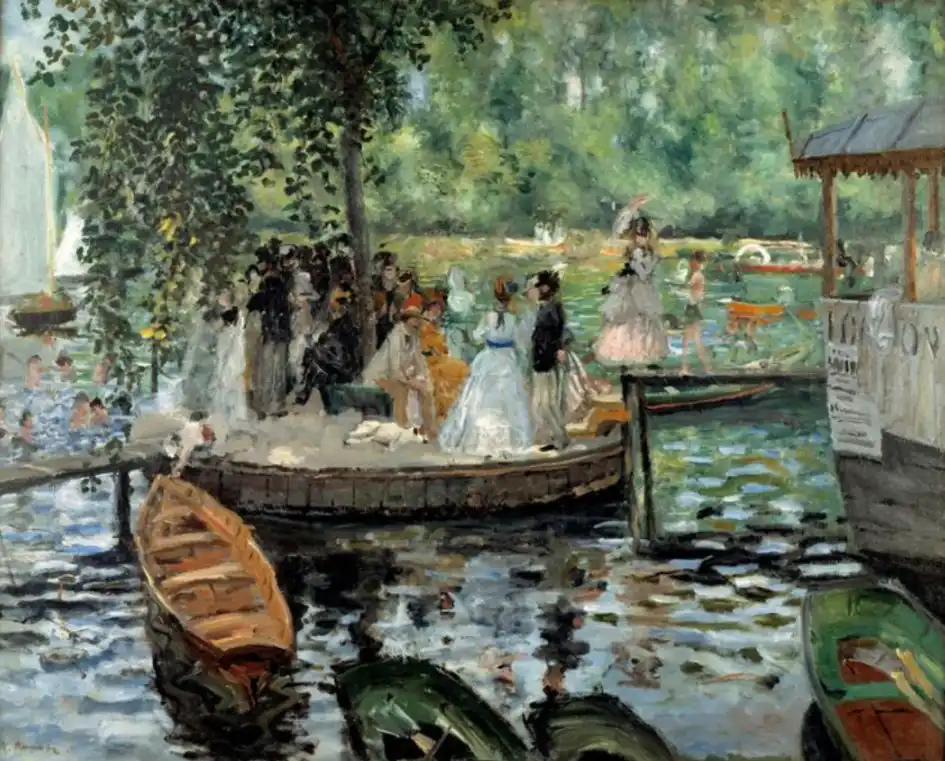
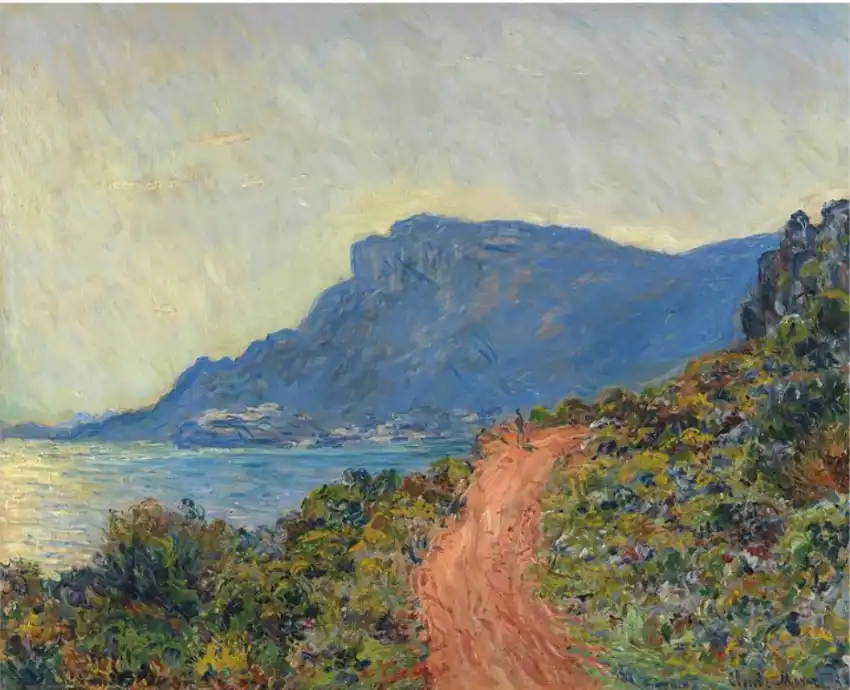
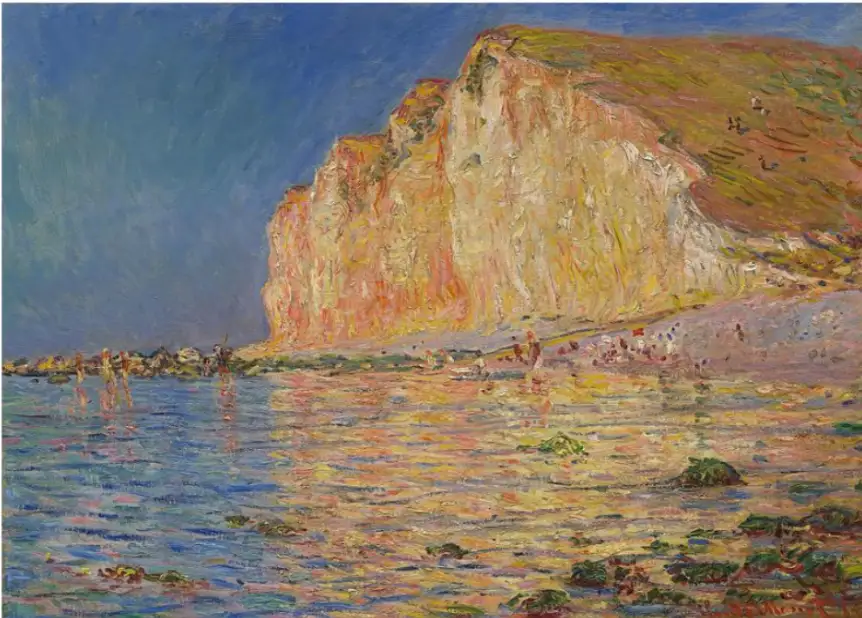
The period from the 1860s until the 1890s was the real time of this art movement. The style that was started was loose brushwork that displays paint texture and vivid colors, which shows both the natural illumination and the environmental influences.
The French movement of Impressionism emerged as a protest against academic painting’s strict formal rules during the 1860s to the 1890s period. The art establishment during that period showed a preference for realistic paintings depicting historical and religious content. The artists rejected traditional subjects to focus their work on ordinary environments like parks, cafes, and riversides.
Their painting method involved visible fast brushwork, which portrayed both light reflections across water surfaces and color transitions during sunset hours. These artists conducted their painting process in open-air locations to experience the natural light transformations in front of them. A critic initially called Monet’s Impression Sunrise an “impression” rather than a completed artwork, which became the origin of the term Impressionism. Artists chose to adopt this negative term, which critics originally used to describe Monet’s work as their artistic label.
The Cultural Impact: The art movement of Impressionism introduced a cultural shift that allowed artists to value their individual perception more than strict realistic representation. This style influenced photography alongside fashion illustration.
1907 to 1914 was the cubism time. Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque, and Juan Gris stood as the most influential artists of this art movement. It shows geometric shapes, overlapping planes, and multiple perspectives at once. The artwork Les Demoiselles d’Avignon (1907) stands as one of the most important examples from Pablo Picasso’s artistic production.
Cubism introduced an unprecedented visual method to painting through its abandonment of traditional single-perspective depictions. During this period, artists transformed objects into geometric forms, including cubes and cones, and cylinders, before presenting multiple viewpoints to the audience.
Picasso studied African masks while Braque studied Paul Cézanne’s geometric techniques, which led to the development of Cubism. The new artistic style transformed painting practices while inspiring architects and sculptors, as well as designers who worked in graphic design.
The cultural impact of Cubism led to a transformation in representation practices while its ideas influenced modern advertising layouts, abstract sculpture, and World War I camouflage designs.
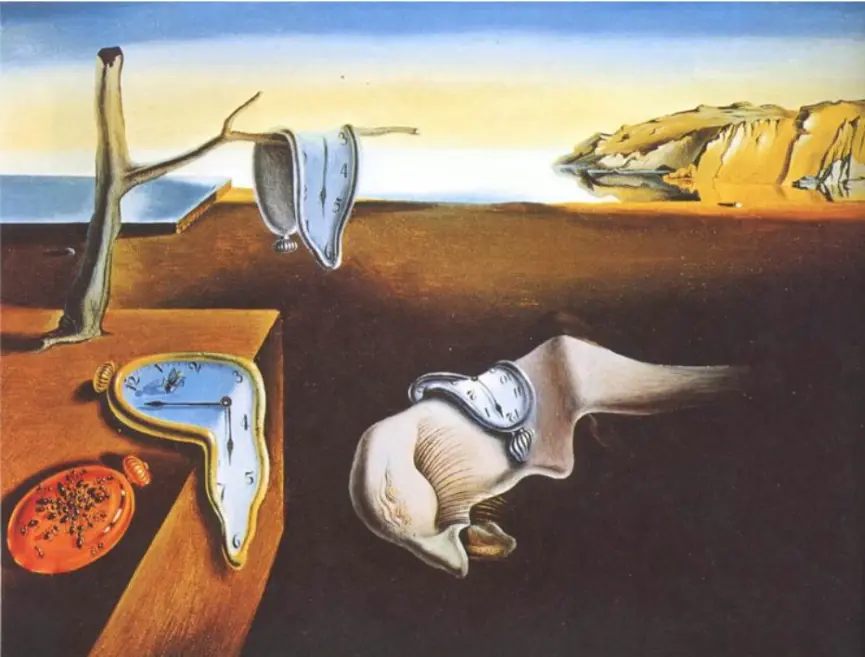
The Surrealist movement developed from 1920 to 1930. The artwork displays surreal elements that combine with unexpected juxtapositions to derive their meaning from subconscious mental processes. The Surrealist movement received its core membership from Salvador Dalí and René Magritte, and Max Ernst. Salvador Dalí created The Persistence of Memory in 1931 as a defining Surrealist masterpiece. Surrealism emerged from the psychoanalytic theory of Sigmund Freud, who studied dreams and unconscious mental processes and hidden desires.
Surrealist artists investigated subconscious mental areas because they believed irrational thoughts could expose inner truths. The artwork shows unusual arrangements through its depiction of melting clocks and floating objects, and massive apples trapped in small spaces and hidden faces. The artists painted these strange scenes with precise detail to create an uncanny feeling of reality for impossible elements. Surrealists employed automatic drawing techniques and collage to avoid logical thinking while allowing their subconscious mind to freely express itself.
The cultural impact: Surrealism influenced film through Alfred Hitchcock’s dream sequences and fashion through Elsa Schiaparelli’s surreal gowns, while also affecting advertising through dreamlike imagery used for attention-grabbing purposes.
These works had no fixed subject. These works used scale and color movement to communicate raw emotional experiences. Pollock used his famous artistic technique by placing canvases on the floor to throw paint in all directions, which turned painting into a performance. The cultural movement of Abstract Expressionism expressed postwar freedom while promoting individuality, which later inspired modern graphic design and fashion print production.
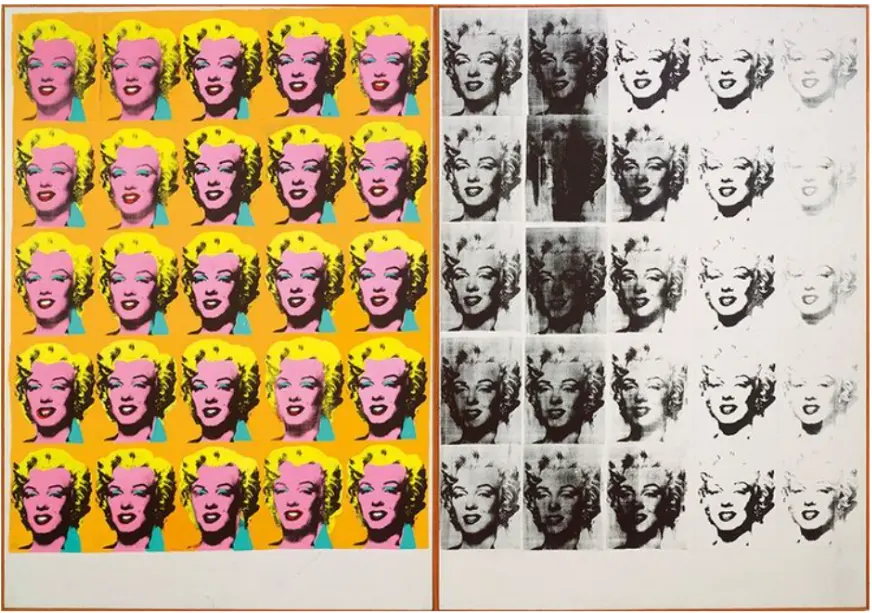
The era of pop art started 1950s till the 1960s. Andy Warhol, Roy Lichtenstein, and Richard Hamilton are famous for this art movement. Bright colors, bold lines, imagery from advertisements, comics, and celebrity culture were their unique style in this artwork. Marilyn Diptych (1962) by Andy Warhol is considered one of the famous works of pop art.
During the Pop Art movement, artists both praised and analyzed the development of consumerism. Pop artists took their inspiration from mass media by creating paintings of everyday objects and comic book panels, together with images of Elvis Presley and Marilyn Monroe.
Warhol achieved mass production effects through his silk-screening technique, which produced identical images across multiple prints. Lichtenstein brought comic book art into large paintings using the same Ben-Day dot pattern that printing technology produced. The movement eliminated traditional distinctions between artistic works of high standing and mass-produced media, thus challenging what people consider art. Through Pop Art, we now view branding differently, while its visual influence extends to graphic design and streetwear, and music album cover production.
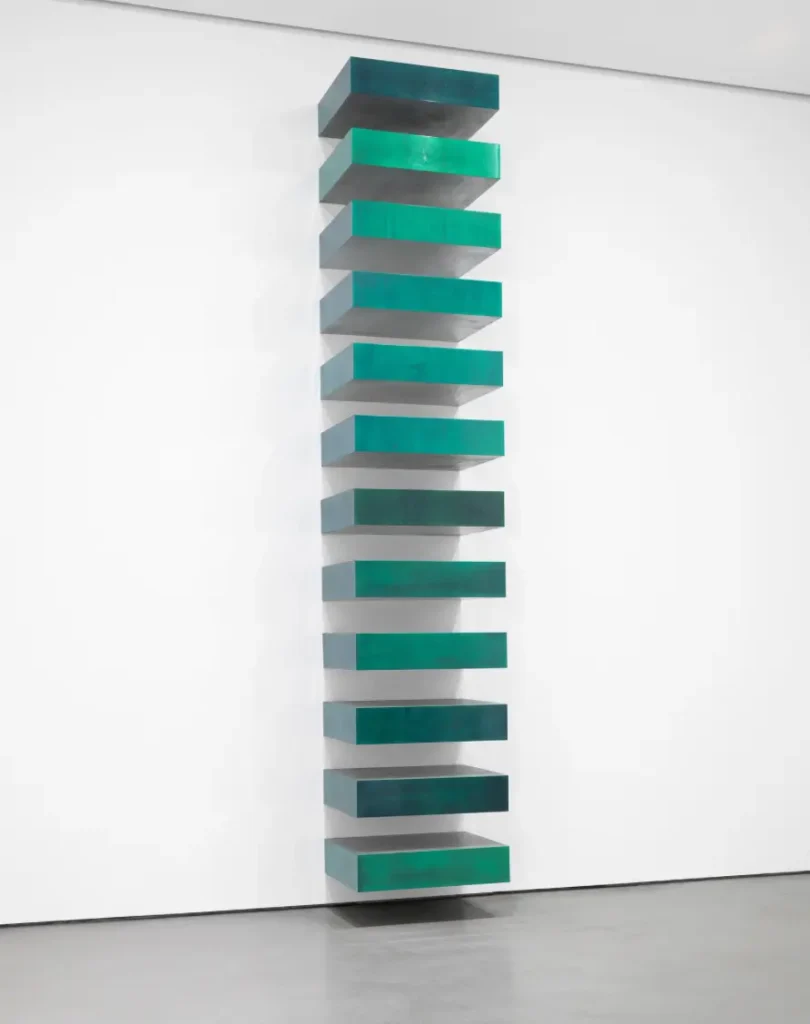
The 1960s to 1970s were Minimalism’s best era. It shows Simplicity, repetition, clean geometric forms, and a limited color palette. The famous Artists Donald Judd, Agnes Martin, and Dan Flavin were renowned for this art. Judd’s untitled metal and Plexiglas stacks are one of their best art examples..
These artists who followed Minimalism as a movement rejected the expressive, emotional style of Abstract Expressionism. The artists of Minimalism dedicated their work to studying pure forms alongside the spatial dimensions they occupied. Artists employed industrial materials consisting of steel, glass, and fluorescent lights, which they organized into basic patterns. The artists eliminated all personal elements to reveal the object in its unadulterated state and its relationship with its spatial surroundings. The Minimalist movement maintains its impact on contemporary architecture and product design, and fashion through its fundamental principle that design benefits from minimalism because less often produces more.
The various artistic movements and styles present in modern art can be organized into major categories, which simplify the understanding of this period. The overview explains the main artistic goals together with the philosophical foundations that motivated artists throughout these movements. Here are some modern art types & styles below:
This art style rejects realistic representation to prioritize the artist’s inner emotions and psychological condition. The artist employs color along with brushwork and form as emotional tools for artistic expression. Through their artwork, the artist aims to create a specific emotional impact on viewers, which might include powerful or untamed feelings.
The artistic movements which align with this category include Fauvism, which employs vivid unnatural colors for emotional representation, and Expressionism, which warps reality to depict psychological distress, as well as Abstract Expressionism, which uses painting’s raw process to convey emotions through works like Jackson Pollock’s chaotic splatters and Mark Rothko’s serene color fields.
The fundamental artistic elements of line, shape, form, and space define this art category. Artists in this group chose to concentrate on the arrangement of their subjects instead of focusing on their subjects themselves. Artists rejected conventional perspective and composition rules to discover fresh visual communication methods.
Cubism breaks objects into geometric planes, while Futurism uses formal techniques to display motion and speed, and Constructivism is a Russian movement that uses geometric shapes for social and political purposes. These artistic movements established the foundation for abstract art to exist as meaningful and complete art forms.
Art goes beyond visual content that appears on the canvas. The true artistic value exists within the conceptual foundation of the work. Through their artistic work, artists used to contest social and cultural norms as well as the nature of art itself and its definitions.
Dadaism functions as an anti-art movement that mocks tradition and logic, while Surrealism studies subconscious ideas and irrational thinking, and Pop Art examines consumer culture and media fame. These art movements maintain their own unique visual identity, yet their core strength emerges from their powerful intellectual concepts.
This artistic style connects to the external world through innovative modern perspectives. These artists dedicated their work to studying how people perceive and perceive the world. The artists focused on expressing particular moments or sensations, or perceptions, instead of creating perfect representations of reality.
Impressionism focuses on immediate light effects and color perceptions in the present, while Post-Impressionism adds personal subjective elements to Impressionist ideas. The two movements fit within this category.
Modern art exists beyond being a collection of unusual paintings since it operates through several distinct categories. Artists of the modern era engaged in a dialogue about two central questions: What defines art, and what form can it take? Modern art demonstrated that the definition of art evolved into a dynamic exploration of new discoveries rather than a fixed definition.
The modern art movement period consisted of more than various artistic styles because it represented a complete revolutionary dialogue that lasted for over a century. The period developed into a complete revolutionary movement, which maintained a hundred-year dialogue. Modern art emerged when Impressionists started painting sunset light until Pop Artists adopted comic strip colors, thus breaking free from traditional art conventions to ask new questions.
Artists during the late 1800s through the 1970s shifted away from realistic art to pursue abstract forms and personal artistic expression, and innovative techniques.
The 7 types of movement are Impressionism, Post-Impressionism, Cubism, Surrealism, Abstract Expressionism, Pop Art, and Minimalism.
The 6 modern art styles and examples include Impressionism (Monet), Cubism (Picasso), Surrealism (Dalí), Abstract Expressionism (Pollock), Pop Art (Warhol), and Minimalism (Judd).
The famous modern art movements include Impressionism, Cubism, Surrealism, Abstract Expressionism, Pop Art, Minimalism, and Post-Impressionism.